1. Investment Summary
IonQ represents a high-risk, high-reward investment opportunity in the nascent quantum computing industry. The company shows strong revenue growth trajectories (95.4% in 2024) but faces significant operating losses that continue to widen (-$331.6M in 2024). While IonQ possesses technological leadership in trapped-ion quantum computing and maintains a solid balance sheet with $340.3M in cash and investments, the path to profitability remains uncertain. Given the early-stage nature of quantum computing commercialization, intensifying competition, and substantial ongoing R&D requirements, IonQ is recommended for investors with high risk tolerance and long investment horizons.
2. Company Overview
IonQ, founded in 2015 and headquartered in College Park, Maryland, is pioneering the development of general-purpose quantum computing systems. The company has commercialized 20-qubit quantum computers, making them accessible through major cloud platforms including Amazon Web Services' Amazon Braket, Microsoft's Azure Quantum, and Google's Cloud Marketplace, as well as through its cloud service.
IonQ differentiates itself through its trapped-ion approach to quantum computing, which uses charged atoms (ions) suspended in electromagnetic fields to form qubits. This technology offers advantages in qubit coherence time and gate fidelity compared to competing approaches. The company emerged from research at the University of Maryland and Duke University and went public via SPAC in 2021.
3. Competitive Positioning
IonQ's competitive strengths include:
Technological Approach: IonQ's trapped-ion technology offers superior qubit stability and error rates compared to some competing technologies. This approach enables potentially longer coherence times, which is crucial for complex quantum calculations.
Cloud Platform Integration: Partnerships with all major cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google) give IonQ broad access to enterprise customers without requiring significant direct sales infrastructure.
Academic Foundations: Strong ties to research institutions provide access to talent and cutting-edge theoretical developments.
However, IonQ faces intense competition from:
Tech Giants: IBM, Google, and Microsoft are investing billions in competing quantum technologies with vastly greater resources.
Other Quantum Startups: Rigetti, D-Wave, and PsiQuantum are pursuing alternative quantum computing approaches.
International Competition: Chinese and European entities are heavily investing in quantum technologies with significant governmental support.
4. Opportunities
IonQ's growth opportunities include:
Quantum Computing as a Service (QCaaS): Expanding cloud-based quantum computing offerings to reach more enterprises experimenting with quantum applications.
Industry Verticals: Developing specialized quantum solutions for high-value industries including pharmaceuticals, materials science, logistics, and financial services.
Algorithmic Development: Creating proprietary quantum algorithms that demonstrate clear advantages over classical computing approaches.
Hardware Scaling: Advancing qubit count and quality to reach quantum advantage in commercially relevant applications before competitors.
Government Contracts: Securing additional U.S. government funding as quantum computing is increasingly viewed as strategically important.
5. Risks
Significant investment risks include:
Path to Profitability: Deepening losses (-$331.6M in 2024 vs -$157.8M in 2023) with no clear timeline to profitability.
Technological Uncertainty: The "winning" quantum computing approach remains undetermined, and IonQ's trapped-ion technology faces scaling challenges.
Commercialization Timeline: Practical, revenue-generating quantum applications may be further away than investor expectations suggest.
Resource Disadvantage: IonQ's R&D budget, while growing rapidly, remains far smaller than those of large tech competitors.
Talent Competition: Fierce competition for limited quantum computing expertise may increase operational costs.
Market Overexuberance: Current valuations may reflect speculative excitement rather than near-term business fundamentals.
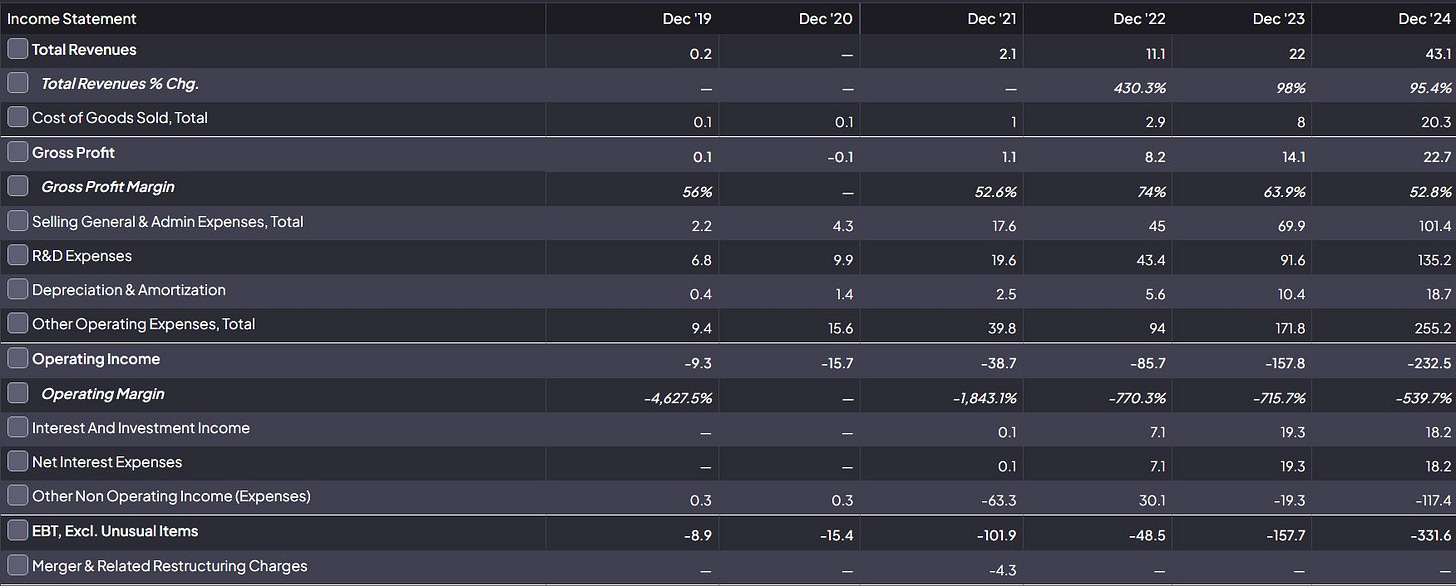
6. Financial Analysis
The financial data reveal a company in early commercialization with rapidly increasing revenues but significantly expanding losses:
Revenue Growth:
Revenue has grown from $0.2M in 2019 to $43.1M in 2024, representing extraordinary percentage growth.
2024 saw a 95.4% year-over-year increase from 2023's $22M.
Growth rate remains strong but is decelerating (95.4% in 2024 vs. 98% in 2023).
Profitability and Margins:
Gross profit has improved to $22.7M in 2024, with a 52.8% gross margin.
Despite this, operating losses have expanded dramatically to -$232.5M in 2024 from -$157.8M in 2023.
Net losses reached -$331.6M in 2024, more than doubling from -$157.8M in 2023.
Operating margin remains deeply negative at -539.7%, though improved from earlier years.
Expense Structure:
R&D expenses have grown substantially to $135.2M in 2024, reflecting the company's technology-focused strategy.
SG&A expenses reached $101.4M in 2024, up from $69.9M in 2023.
Total operating expenses rose to $255.2M in 2024 from $171.8M in 2023.
Cash Flow and Operations:
Cash from operations remains negative at -$105.7M in 2024, worsening from -$78.8M in 2023.
Despite operating losses, stock-based compensation has increased significantly to $106.9M in 2024.
Balance Sheet Strength:
Total cash and short-term investments of $340.3M in 2024 provide runway despite substantial losses.
Property, plant, and equipment have increased to $62.2M, reflecting investments in manufacturing capabilities.
Total current assets stand at $378.8M, providing adequate liquidity for near-term operations.
The company has increased its investment in physical infrastructure, with gross PPE growing to $89.8M in 2024.
7. Investment Outlook
The investment outlook for IonQ is characterized by both significant potential and substantial uncertainty:
Short-Term (1-2 Years):
Continued revenue growth but likely acceleration in losses as R&D and commercialization efforts intensify.
Stock price volatility is tied to quantum computing news, technology demonstrations, and broader tech market sentiment.
Cash burn will require careful monitoring of the remaining operational runway.
Medium-Term (3-5 Years):
Potential for breakthrough quantum applications that demonstrate commercial viability.
Increasing competition as quantum computing approaches commercial relevance.
Possible industry consolidation with acquisition opportunities or threats.
Long-Term (5+ Years):
Potential for exponential value creation if quantum advantage is achieved in commercially relevant applications.
Possibility of strategic acquisition by larger technology companies seeking quantum capabilities.
Risk of technological obsolescence if alternative quantum approaches prove superior.
8. Conclusion and Recommendation
IonQ represents a speculative investment opportunity in the emerging quantum computing field with potentially revolutionary long-term implications. The company demonstrates promising revenue growth and technological accomplishments but faces widening losses and intense competition.
Recommendation:
Speculative Buy for investors with high risk tolerance and long-term horizons who can withstand significant volatility.
Position sizing should be limited to a small portion of a diversified portfolio.
Investors should be prepared for the possibility of additional capital raises that may dilute ownership.
Regular reassessment is necessary as the quantum computing competitive landscape evolves rapidly.
The quantum computing industry may represent one of the most significant technological opportunities of the next decade, but successful investments will require patience, risk tolerance, and careful attention to both technological and commercial developments.






.+