1. Executive Summary
Tesla, Inc. is a leading innovator in the electric vehicle (EV) and renewable energy sectors. With a $1.287 trillion market capitalization and a P/E ratio of 106.86, Tesla commands a significant premium in the market, reflecting its dominant position and future growth potential. The company’s diversified portfolio includes electric vehicles, energy storage solutions, and solar energy products, enabling it to target multiple high-growth markets. However, such valuations necessitate scrutiny of Tesla's financial performance, operational efficiency, and future prospects.
2. Financial Overview
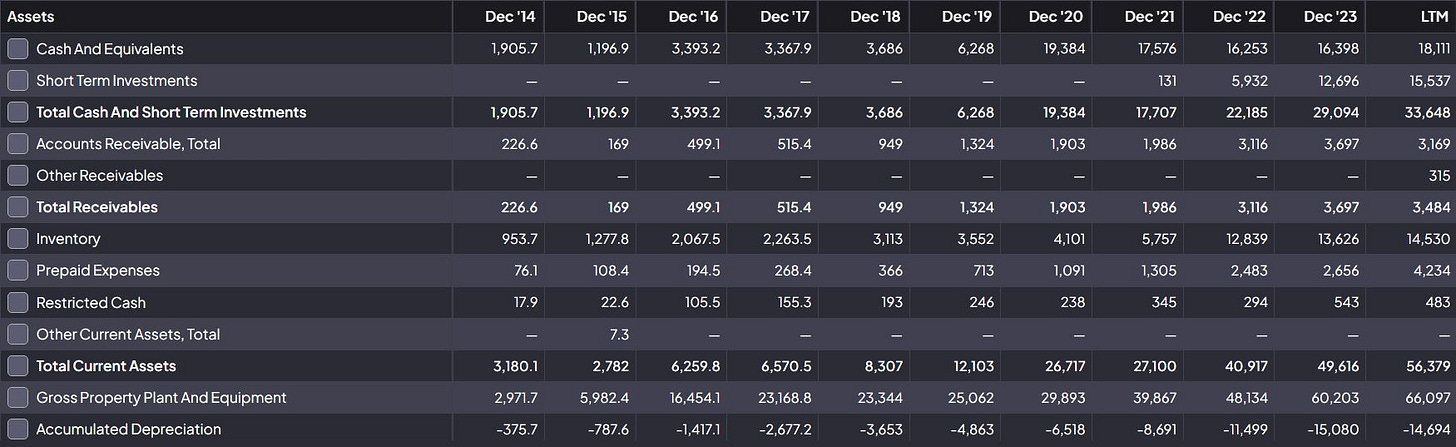
Balance Sheet Analysis (2014–LTM 2023)
Assets Growth: Tesla has demonstrated substantial growth in total current assets, expanding from $3.18 billion in 2014 to $56.38 billion in the latest 12 months (LTM). The growth reflects robust cash and equivalents ($18.11 billion LTM) and increasing accounts receivables ($3.48 billion LTM), supporting operational liquidity.
Inventory Management: Inventory rose significantly to $14.53 billion, showcasing Tesla’s expanding production capabilities but raising questions about turnover efficiency.
Fixed Assets: Tesla’s investment in property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) reached $66.1 billion (LTM), underscoring its commitment to scaling production and innovation.
Debt Risks: Tesla’s total liabilities (not explicitly detailed here but deducible) suggest close monitoring of debt ratios, although restricted cash and robust cash reserves mitigate immediate risks.
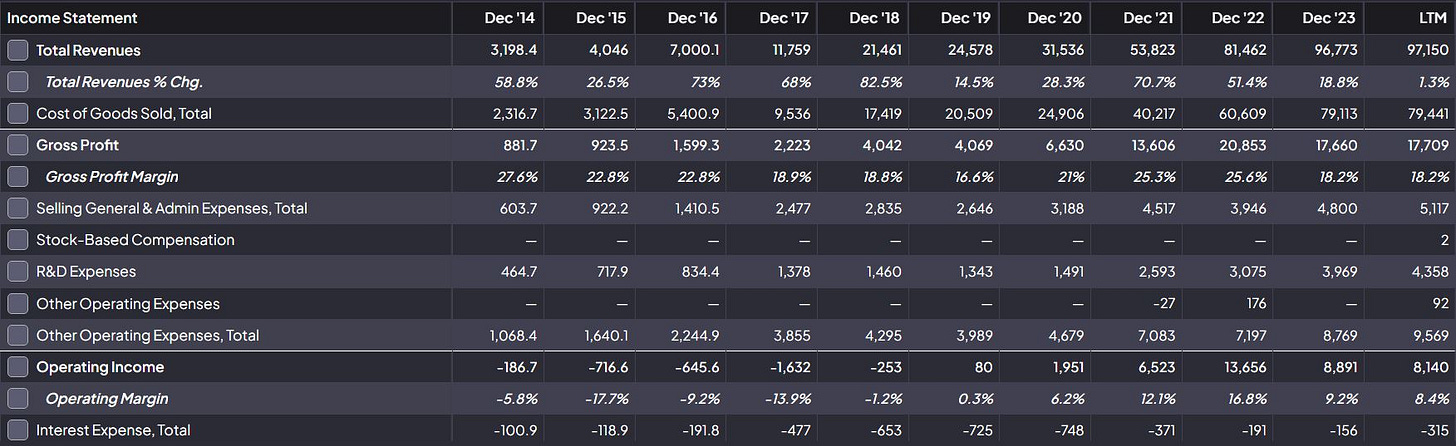
Income Statement Analysis (2014–LTM 2023)
Revenue Growth: Revenues increased from $3.2 billion in 2014 to $97.15 billion LTM, reflecting a 30x growth driven by increasing EV adoption, energy storage sales, and regulatory credits.
Gross Margins: Gross profit margins have stabilized at 18.2% LTM, compared to historical volatility (low 16.6% in 2019 to a high of 25.6% in 2022). This stabilization is vital as Tesla scales its operations globally.
Operating Income: Operating margins have improved to 9.8% (LTM) from negative values in the mid-2010s, reflecting operational efficiencies and scale advantages.
R&D Investments: Tesla maintains a commitment to innovation, with R&D expenses rising to $4.36 billion (LTM), ensuring sustained leadership in EV technology.
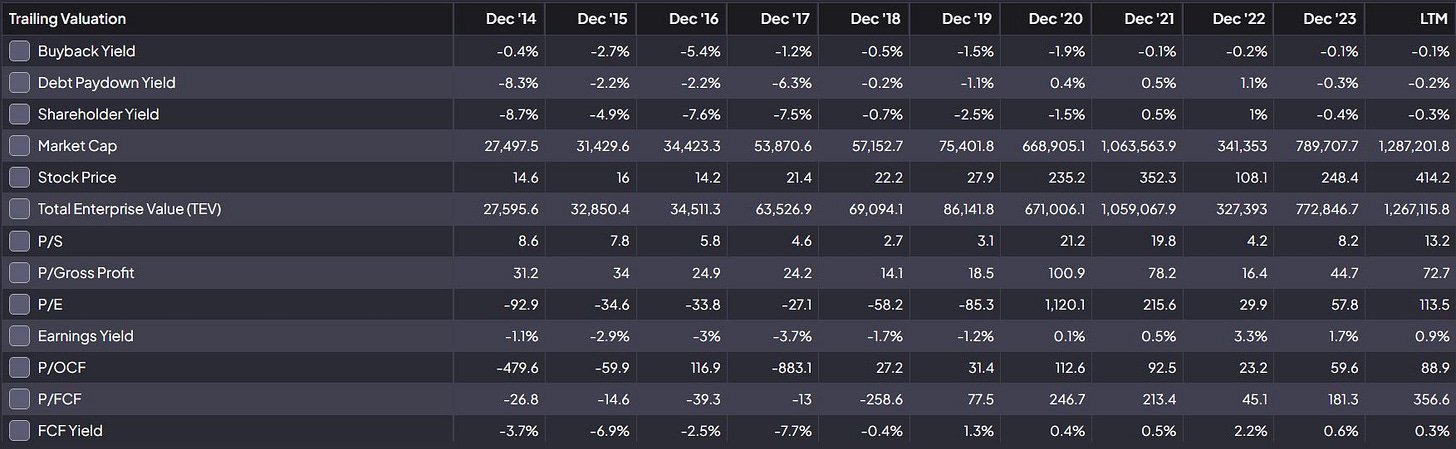
Valuation Metrics (2014–LTM 2023)
Tesla’s valuation metrics (P/E 106.86, P/S 13.2) underscore its premium, fuelled by future growth expectations. However, a comparison to industry peers highlights a stretched valuation, requiring sustained revenue growth and margin expansion to justify current prices.
3. Competitive Positioning
Automotive Segment
Market Leadership: Tesla is the global EV leader, with competitive advantages in battery technology, proprietary software, and direct sales channels.
Expansion Plans: Tesla's gigafactories in strategic locations bolster production capabilities and reduce costs per vehicle.
Supercharger Network: The proprietary network supports customer retention and enhances brand value.
Energy Segment
Growing Market: With increasing emphasis on renewable energy, Tesla’s energy storage solutions (e.g., Powerwall, Megapack) and solar products position it to capture market share.
Synergies: The energy business benefits from Tesla’s brand strength and aligns with global decarbonization trends.
4. Risks
Valuation Concerns: With a P/E exceeding 100x, any deceleration in revenue growth could lead to a significant valuation contraction.
Competition: Traditional automakers (e.g., Ford, GM) and EV-centric firms (e.g., Rivian, Lucid) are scaling EV production, narrowing Tesla’s first-mover advantage.
Macroeconomic Headwinds: Inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical tensions could affect consumer demand and supply chains.
Regulatory Dependence: A significant portion of Tesla's revenues historically comes from regulatory credits, which could diminish as competitors meet compliance standards.
5. Investment Outlook
Bull Case
Revenue Expansion: Tesla’s consistent revenue growth, supported by scaling production and geographic expansion, underpins a bullish narrative.
Technology Leadership: Advancements in autonomous driving, battery innovation, and energy storage ensure Tesla remains at the forefront of technological breakthroughs.
Sustainability Tailwinds: Global shifts toward EV adoption and renewable energy strongly favour Tesla’s business model.
Bear Case
Overvaluation: Current market premiums may not withstand competitive pressures or economic downturns.
Execution Risks: Rapid expansion introduces risks of operational inefficiencies or overextension.
Margin Pressures: Increased competition may compress margins in both the automotive and energy segments.
6. Conclusion
Tesla represents a unique investment opportunity, combining industry leadership, innovation, and exposure to high-growth markets. However, its stretched valuation requires continued operational excellence and revenue expansion. Investors should weigh Tesla's transformative potential against its elevated risk profile, particularly in the context of increasing competition and macroeconomic volatility.
This thesis favours a long-term bullish stance on Tesla, contingent on steady margin improvement, innovation leadership, and robust financial performance.




What impact will rising competition in EVs have on Tesla's margins?